Seizure Prediction in Epilepsy
Research Assistant, Supervisors: Prof. Raymond HF CHAN, Prof. Ho Man CHAN, Prof. Bee Luan KHOO, HK COCHE
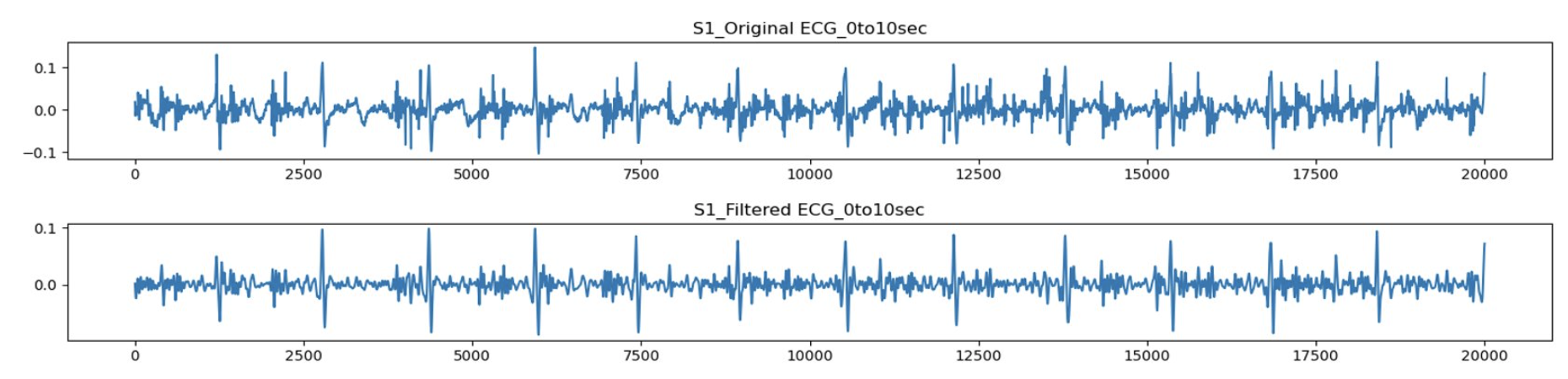
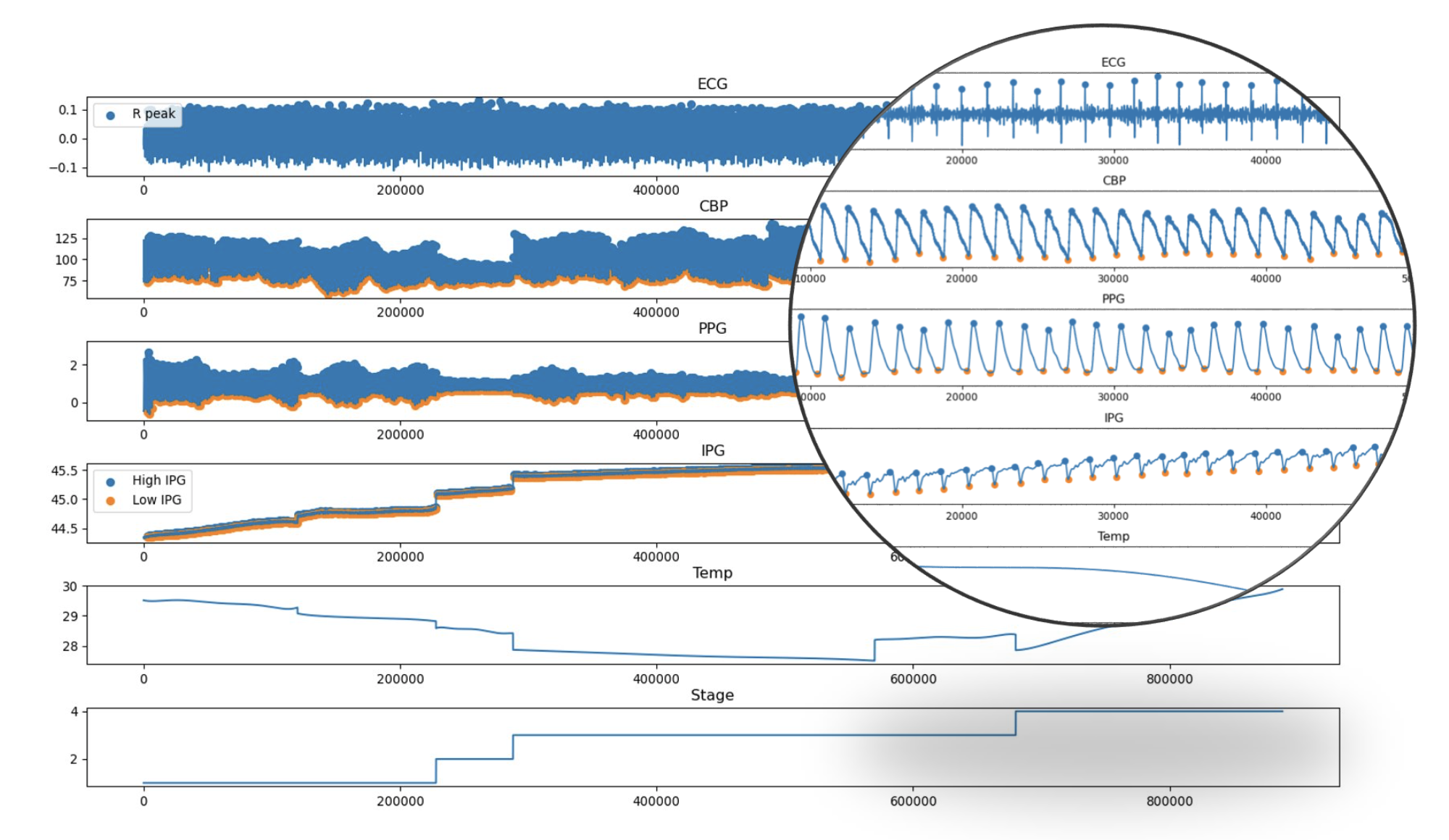
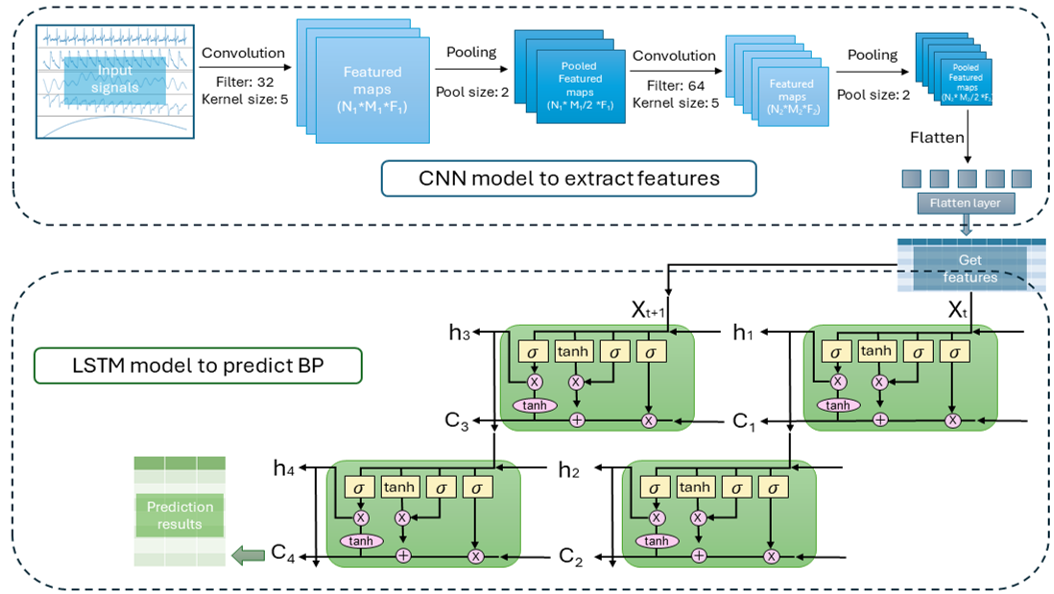
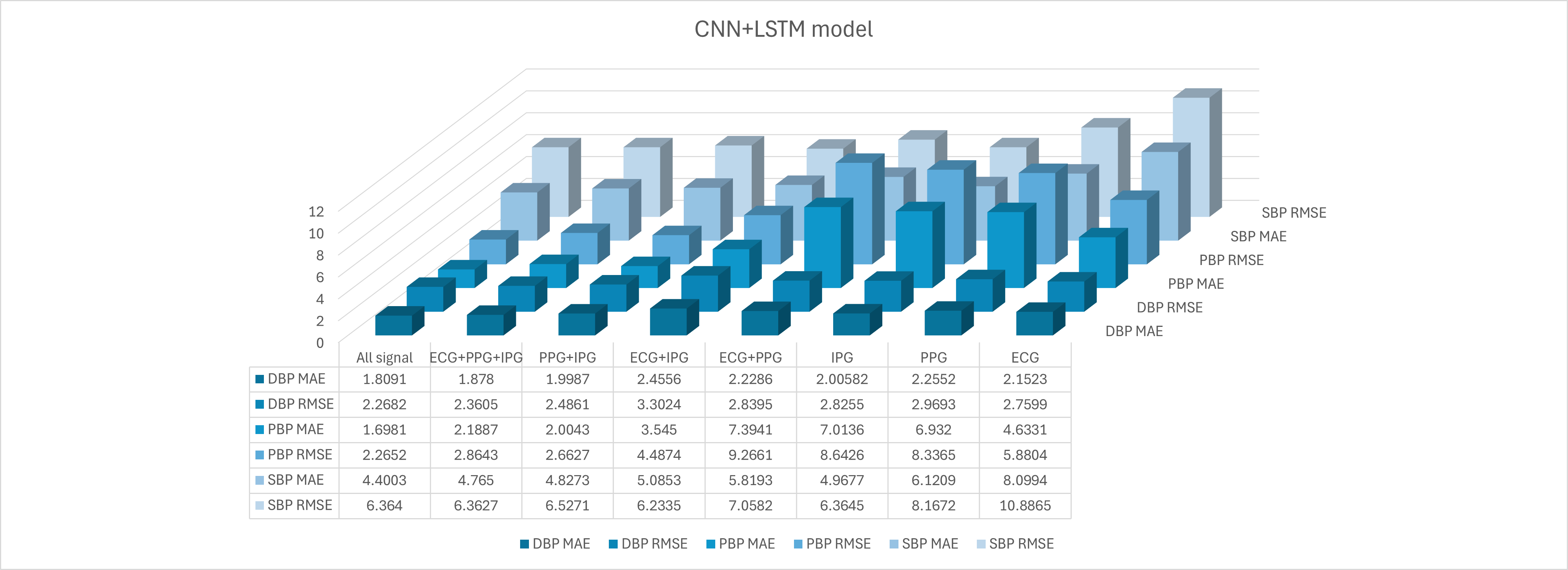
This is part of Ms. HUANG Ke’s PhD program at City University of Hong Kong, where we are focused on using EEG and other multi-modal signals from open-access datasets to predict epileptic seizures using machine learning models. My contributions to this project include the following tasks:
- Dataset Selection: I conducted extensive research to identify suitable open-access datasets and made selections based on EEG channels.
- Feature Extraction: I utilized EEGLab and the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) method to extract relevant features from the EEG data.
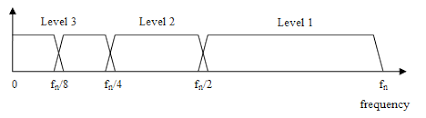
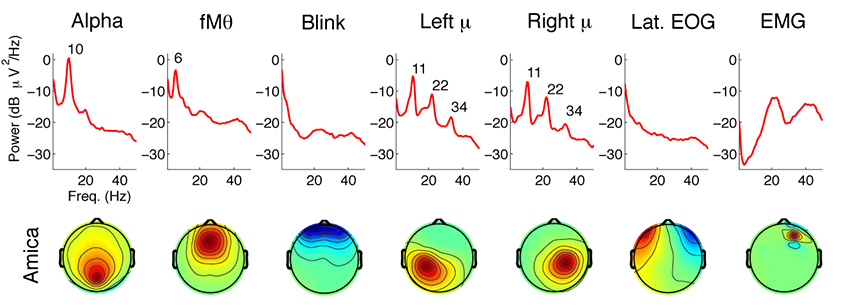
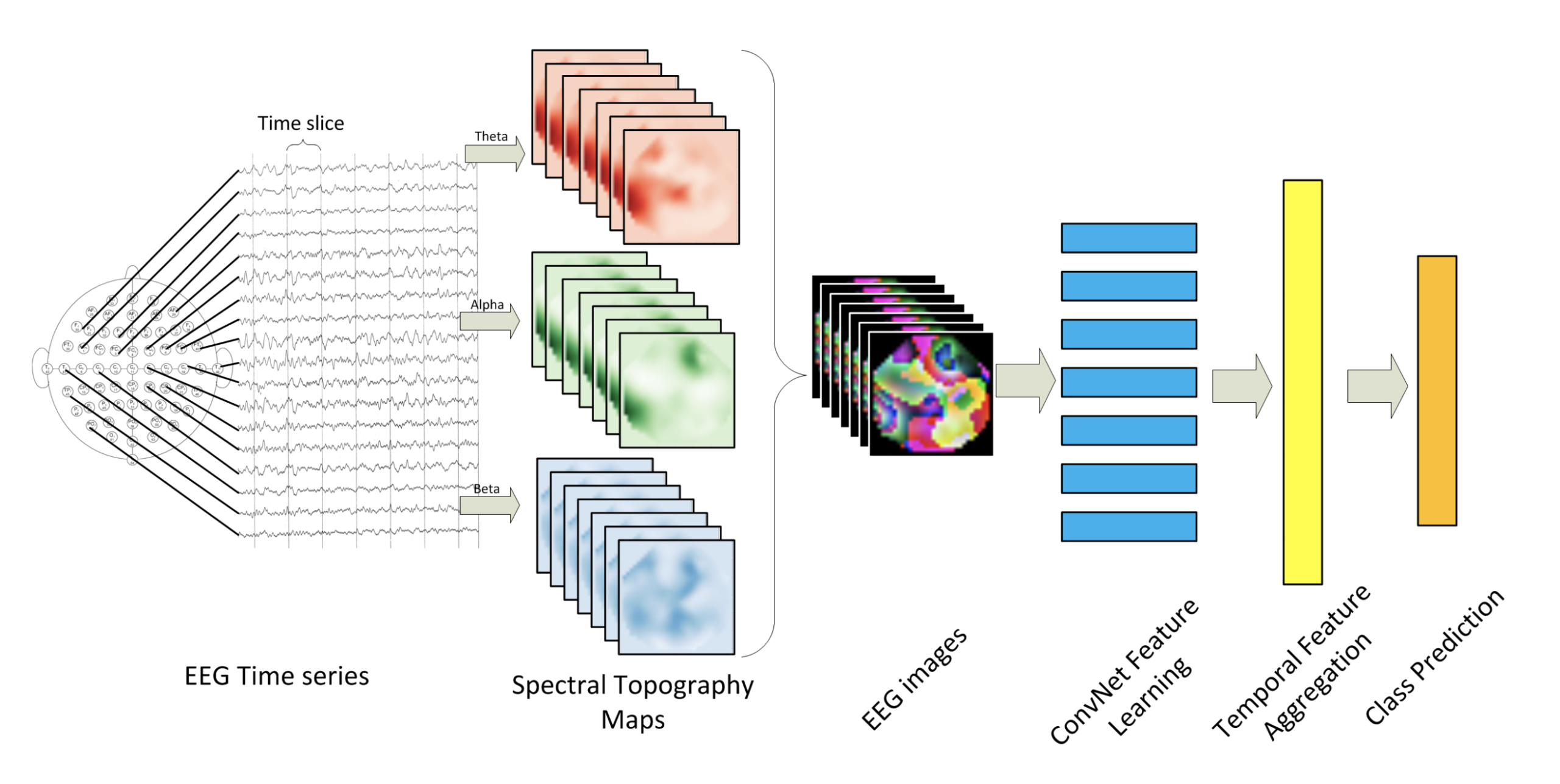
- Deep Learning-Based Feature Extraction: I explored deep learning techniques for feature extraction from the multi-modal signals.

 U of Minnesota
U of Minnesota